Veterinary medicine

APPLICATIONS AND BENEFITS
IN EQUINE MEDICINE
PetCellpen® BENEFITS
For the veterinarian
- Cutting-edge technology for everyday use
- No consumables or disposables
- Wireless and lightweight (250g)
- Reduced use of antibiotics
- Results from the very first session
- Any species, body area and size
- No personal protective equipment required
- Stand-alone or adjunctive therapy to the clinical protocol
- No clipping or post-clipping cleaning
- Short and calm sessions
- Can be used by veterinarians and veterinary nurses
- Easy handling and application
For the patient
- Painless, minimal handling
- No adverse effects
- Treatment is well tolerated
- Reduces the consumption of pharmaceutical products
- Faster healing process
- Combats resistant infections
- Can be used on ulcerated tumours
- Extensive list of indications
- Effective in multi-resistant infections
- Depth of action of more than 1cm
This device is intended for use only by veterinary professionals for the treatment of small animals and horses.
Applications
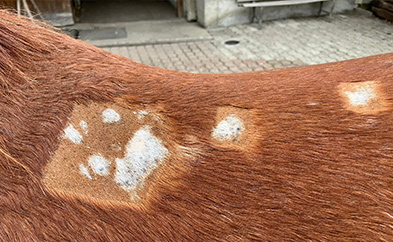
Dermatology
Indications
- Insect bite allergy
- Habronemiasis
- Dermatitis and panniculitis
- Summer eczema (Equine Summer Dermatitis)
- Chronic scabs
The easy-to-handle EquCellpen® allows the veterinary physiotherapist to simultaneously apply direct cold plasma therapy and high-frequency electrotherapy. In this way, the healing of chronic wounds can be stimulated. Patients undergoing rehabilitation after surgery or those with typical sports injuries benefit from an accelerated and improved healing process thanks to the deep penetrating effect of the high-frequency therapy. Sport horses with muscle tension, spasms in the neck or back area as well as painful trigger points can be treated very effectively with EquCellpen® relaxation therapy. The short application times allow this form of therapy to be used in many different ways, and it can be combined well with other healing methods.

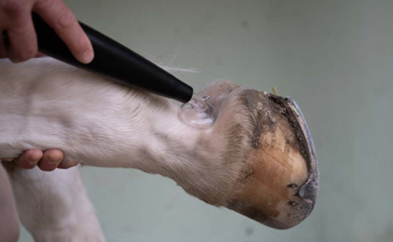
Orthopaedics and physiotherapy
Indications
- Bursitis and oedema
- Desmitis
- Tendon injuries
- Muscle scarring
- Pain in the back (Kissing spines)
- Haematomas / seromas
- Tendinitis and tenosynovitis
- Muscle tension and spasms
- Trigger points
- Post-operative rehabilitation
Treatment with EquCellpen® stimulates the metabolism, reduces swelling and promotes blood circulation. The stimulating effect of the cold plasma on cellular activity promotes regeneration of the injured tissue. The main orthopaedic indications in horses are long-term diseases of the lower limbs, especially tendons and ligaments, which lead to prolonged absences in sport horses. Chronic inflammations can be influenced favourably with the EquCellpen®. Thanks to its simple and wireless handling, the treatment can be carried out irrespective of the location and usually in combination with other measures. The short treatment time with the pen is a key advantage.

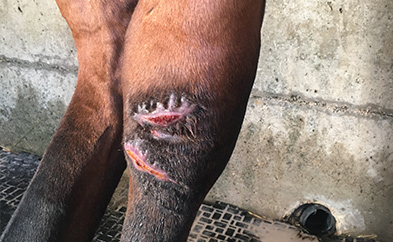
Wound healing
Indications
- Wounds at the corner of the mouth
- Saddle wounds
- Healing problems
- Burns
- Scar treatment
- Abscesses
In dermatology, the plasma produced by the EquCellpen® has an antiseptic and anti-inflammatory effect. Cold atmospheric plasma has a proven and painless effect against bacteria, fungi and viruses. Bacterial dermatitis, in particular generalized malaria in horses, can be effectively treated with EquCellpen®. Chronic wounds, including those on exposed sites, can be healed due to the debridement effect on the one hand and the stimulation of cellular activity that promotes granulation on the other hand. Epithelialization is more organised, resulting in better quality repair tissue. As cold plasma can also reduce itching, it is ideal for improving the symptoms of itch and other allergy-related dermatitis.

All clinical cases
Download all successful clinical cases in equine medicine.
Therapeutic guide
Detailed instructions for use and according to therapeutic application.
Bibliography
Antimicrobial effects: Bacteria
- Brun P, Bernabè G, Marchiori C, Scarpa M, Zuin M, Cavazzana R, Zaniol B, Martines E. Antibacterial efficacy and mechanisms of action of low power atmospheric pressure cold plasma: membrane permeability, biofilm penetration and antimicrobial sensitization. J Appl Microbiol. 2018 Aug;125(2):398-408. PMID: 29655267. doi: 10.1111/jam.13780
- Haghighi L, Azizi A, Vatanpour M, Ramezani G. Antibacterial Efficacy of Cold Atmospheric Plasma, Photodynamic Therapy with Two Photosensitizers, and Diode Laser on Primary Mandibular Second Molar Root Canals Infected with Enterococcus faecalis: An in Vitro Study. Int J Dent. 2023 Apr 21:2023:5514829. PMID: 37123349. doi: 10.1155/2023/5514829
- Alekseev O, Donovan K, Limonnik V, Azizkhan-Clifford J. Nonthermal Dielectric Barrier Discharge (DBD) Plasma Suppresses Herpes Simplex Virus Type 1 (HSV-1) Replication in Corneal Epithelium. Transl Vis Sci Technol. 2014 Mar 27;3(2):2. PMID: 24757592. doi: 10.10.1167/tvst.3.2.2
- Bunz O, Mese K, Zhang W, Piwowarczyk A, Ehrhardt A. Effect of cold atmospheric plasma (CAP) on human adenoviruses is adenovirus type-dependent. PLoS One. 2018 Oct 26;13 (10):e0202352. PMID: 30365500. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0202352
- Aboubakr HA, Mor SK, Higgins LA, Armien A, Youssef MM, Bruggeman PJ, Goyal SM. Cold argon-oxygen plasma species oxidize and disintegrate capsid protein of feline calicivirus. PLoS One. 2018 Mar 22;13(3):e0194618. PMID: 29566061. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0194618
- Lee T-H, Hyun J-E, Kang Y-H, Baek S-J, Hwang C-Y. In vitro antifungal activity of cold atmospheric microwave plasma and synergistic activity against Malassezia pachydermatis when combined with chlorhexidine gluconate. Vet Med Sci. 2022 Mar;8(2):524-529. PMID: 35089639. doi: 10.1002/vms3.719
- Šimončicová J, Kaliňáková B, Medvecká V, Lakatoš B, Kryštofová S, Hoppanová L, Palušková V, Hudecová D, Ďurina P, Zahoranová A. Cold plasma treatment triggers antioxidative defense system and induces changes in hyphal surface and subcellular structures of Aspergillus flavus. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2018 Aug;102(15):6647-6658. PMID: 29858953. doi: 10.1007/s00253-018-9118-y
- Gnat S, Lagowski D, Dylag M, Zielinski J, Studzinski M, Nowakiewicz A. Cold atmospheric pressure plasma (CAPP) as a new alternative treatment method for onychomycosis caused by Trichophyton verrucosum: in vitro studies. 2021 Dec;49(6):1233-1240. PMID: 34499324. doi: 10.1007/s15010-021-01691-w
- Ten Bosch L, Habedank B, Siebert D, Mrotzek J, Viöl W. Cold Atmospheric Pressure Plasma Comb – A Physical Approach for Pediculosis Treatment. Int J Environ Res Public Health 2018 Dec 21;16(1):19. PMID: 30577656. doi: 10.3390/ijerph16010019
- Daeschlein G, Scholz S, Arnold A, von Woedtke T, Kindel E, Niggmeier M, Weltmann K-D, Jünger M. In Vitro Activity of Atmospheric Pressure Plasma Jet (APPJ) Plasma Against Clinical Isolates of Demodex Folliculorum. IEEE Transactions on Plasma Science, Vol. 38, No. 10, October 2010. doi: 10.1109/TPS.2010.2061870
- Schmidt A, Liebelt G, Striesow J, Freund E, von Woedtke T, Wende K, Bekeschus S. The molecular and physiological consequences of cold plasma treatment in murine skin and its barrier function. Free Radic Biol Med. 2020 Dec: 161:32-49. PMID: 33011275. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2020.09.026
- Chatraie M, Torkaman G, Khani M, Salehi H, Shokri B. In vivo study of non-invasive effects of non-thermal plasma in pressure ulcer treatment. Sci Rep. 2018 Apr 4;8(1):5621. PMID: 29618775. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-24049-z
- Schmidt A, Niessner F, von Woedtke Th, Bekeschus S. Hyperspectral Imaging of Wounds Reveals Augmented Tissue Oxygenation Following Cold Physical Plasma Treatment in Vivo. IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON RADIATION AND PLASMA MEDICAL SCIENCES, VOL. 5, NO. 3, MAY 2021
- T. von Woedtke, A. Schmidt, S. Bekeschus, K. Wende, K.D. Weltmann, Plasma medicine: a field of applied redox biology, Vivo 33 (2019) 1011–1026, doi: 10.21873/invivo.11570
- Schmidt A, von Woedtke T, Vollmar B, Hasse S, Bekeschus S. Nrf2 signaling and inflammation are key events in physical plasma-spurred wound healing. Theranostics. 2019 Jan 30;9(4):1066-1084. PMID: 30867816. doi: 10.7150/thno.29754
- Ding C, Huang P, Feng L, Jin T, Zhou Y, He Y, Wu Z, Liu Y. Immediate intervention effect of dielectric barrier discharge on acute inflammation in rabbit’s ear wound, AIP Advances 10. 2020, 025008. doi: 10.1063/1.5139953
- Haertel B, von Woedtke T, Weltmann K-D, Lindequist U. Non-thermal atmosperic-pressure plasma possible application in wound healing. Biomol Ther (Seoul). 2014 Nov;22(6):477-90. PMID: 25489414. doi: 10.4062/biomolther.2014.105
- Gay-Mimbrera J, Garcia MC, Isla-Tejera B, Rodero-Serrano A, Garcia-Nieto AV, Ruano J. Clinical and Biological Principles of Cold Atmospheric Plasma Application in Skin Cancer. Adv Ther. 2016 Jun;33(6):894-909. PMID: 27142848. doi: 10.1007/s12325-016-0338-1
- Lee S-T, Jang Y-S, Kim U-K, Kim H-J, Ryu M-H, Kim G-C, Hwang D-S. Non-thermal plasma application enhances the recovery of transected sciatic nerves in rats. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2021 Jun;246(11):1287-1296. PMID: 33653158. doi: 10.1177/1535370221996655
- Ding C, Ni L, Liu Q, et al. Cold air plasma improving rheumatoid arthritis via mitochondrial apoptosis pathway. Bioeng Transl Med. 2023;8(1):e10366. doi:10.1002/btm2.10366
- Faramarzi F, Zafari P, Alimohammadi M, et al. Inhibitory Effects of Cold Atmospheric Plasma on Inflammation and Tumor‑Like Feature of Fibroblast‑Like Syn

